February 5th,2025
By Scott Jackson
Arleigh Burke-Class Guided-Missile Destroyer, USS Preble (DDG-88) utilizing its High Energy Laser with Integrated Optical-Dazzler and Surveillance (HELIOS) Weapons System.

Helios is apart of a larger program aimed at the development of Solid State Lasers (SSL). Some of the other lasers being developed include the
-Ruggedized High Energy Laser (RHEL);
-Optical Dazzling Interdictor, Navy (ODIN); -Solid State Laser Technology Maturation (SSL-TM)
-High Energy Laser Counter-ASCM Program (HELCA), for shooting down anti-ship cruise missiles.
All of these I’ve listed are in varying states of development and wont be fielded until a future date however HELIOS has been in a testing phase since 2021 and now has been fully integrated into the combat systems of at least the USS Preble (DDG-88) where it will be used to counter drones, small boat threats and missiles.
The main advantage of the direct energy weapons is the price. Lasers cost about $1 to fire compared to some missiles getting into the tens of millions of dollars.
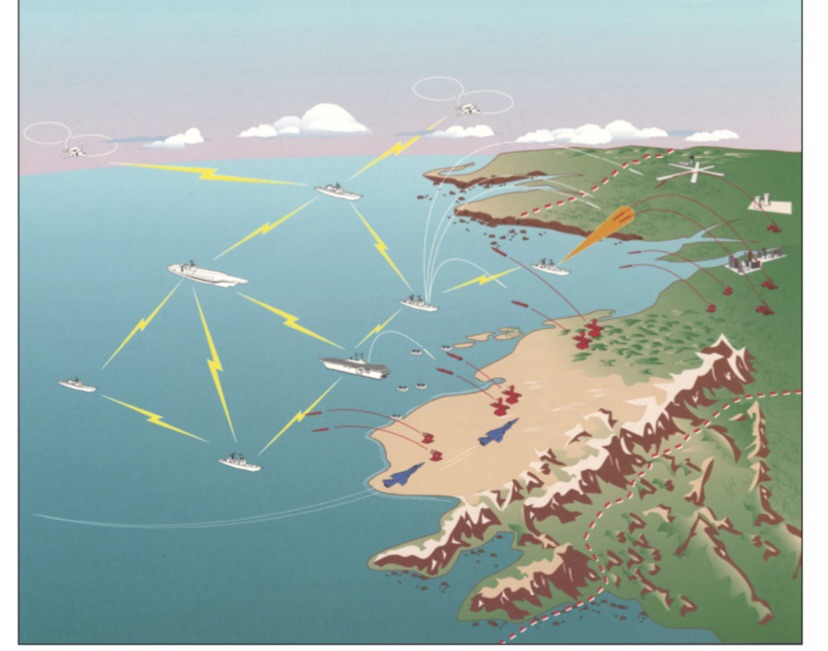
Russias losses in Ukraine for the month of January reached almost 50,000, the second highest since the early days of the war.
According to the General Staff of the Armed Forces of Ukraine in the month of January 2025, the Russian armed forces lost 48,240 soldiers and 573 Russian armored vehicles and 230 tanks. In the Russian order of battle this is roughly equivalent to 3 motorized rifle divisions. In that time the Russian army has managed to take roughly 500 sq. kilometers (193 sq miles) in the Kursk Region as well as Ukraine. These numbers are almost identically to December of 2024 numbers except they took 100km more territory.
The situation in Ukraine remains much as it has the past couple months. Ukrainian forces continues to reinforce defensive points while Russia has kept its army’s pushing into enemy territory. Ukrainian forces have stepped up the intensity of attacks on Russian oil and gas infrastructure, with the Ukrainian security services (USB) targeting the regions of Volgograd and Astrakhan.
Future daily briefs will have more Ukraine reporting as I reconnect with my sources and find new ones.
Iraqi airstrike kills 5 ISIS operatives in Iraq.
On January 31, Iraqi Security Forces (ISF), supported by U.S. Central Command (CENTCOM) forces conducted an airstrike near Kirkuk, Iraq. The attack killed 5 ISIS fighters according to CENTCOM.
“An initial post-strike clearance found multiple explosive suicide belts and other materials,”
CENTCOM confirmed in a statement, underscoring the strike’s role in weakening the group’s operational capabilities.
“ISIS remains a threat to the region and beyond, and CENTCOM, along with partners and allies, will continue to aggressively pursue these terrorists to protect the homeland,”
This operation was backed by Coalition Joint Task Force – Operation Inherent Resolve (CTF-OIR), which provided intelligence and technical support for the strike.
U.S. forces have recently stepped up strikes against ISIS targets since the fall of the Assad Regime in Syria. With the state being weakened it was a possibility that Daesh could attempt a comeback.
On the same note….
US Africa Command carries out airstrikes on ISIS in Somalia.
On February 1st, 2025, US president Donald Trump, in his first major U.S. Strike overseas since he took office, ordered US forces to carry out airstrikes on ISIS targets in Northern Somalia in the Golis Mountains. Defense Secretary Pete Hegseth said that “multiple operatives” were killed in the strike.

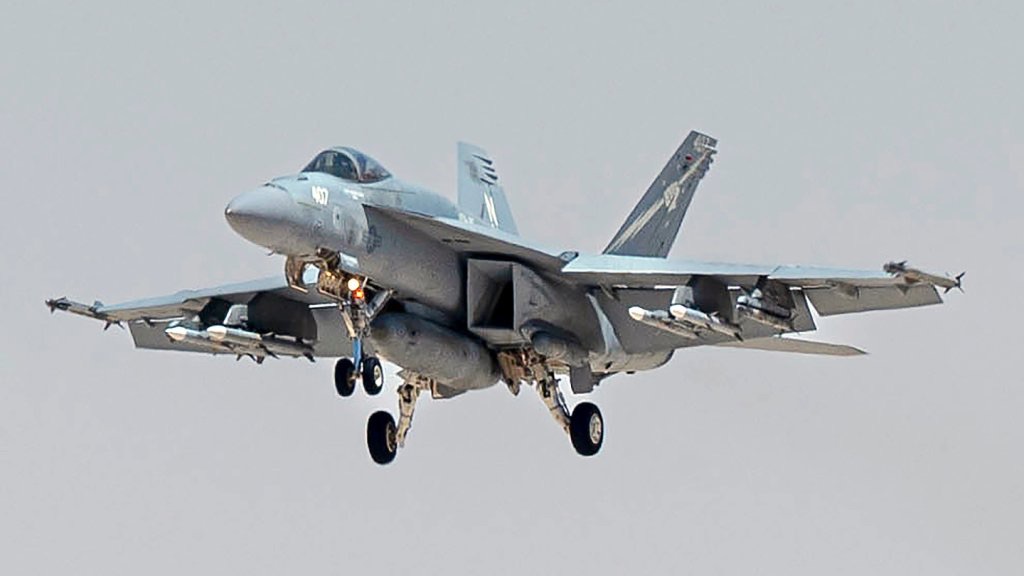
The strikes were carried out by planes from the navy and Air Force. FA-18 Super Hornets took part from the USS Harry S. Truman currently stationed in the Red Sea.
While the main threat in the area has been Al-Shabab, ISIL has been involved in attacks in Southern and Central Somalia. Even while facing the threat of US bombings as well as the policing actions of the Somolian Security Forces, and a fierce rivalry with Al-Shabob ISIS (ISIL) continues to grow and gain a strong foundation in the country.













You must be logged in to post a comment.